Resveralife Reports: Stable Delivery System for Resveratrol Discovered
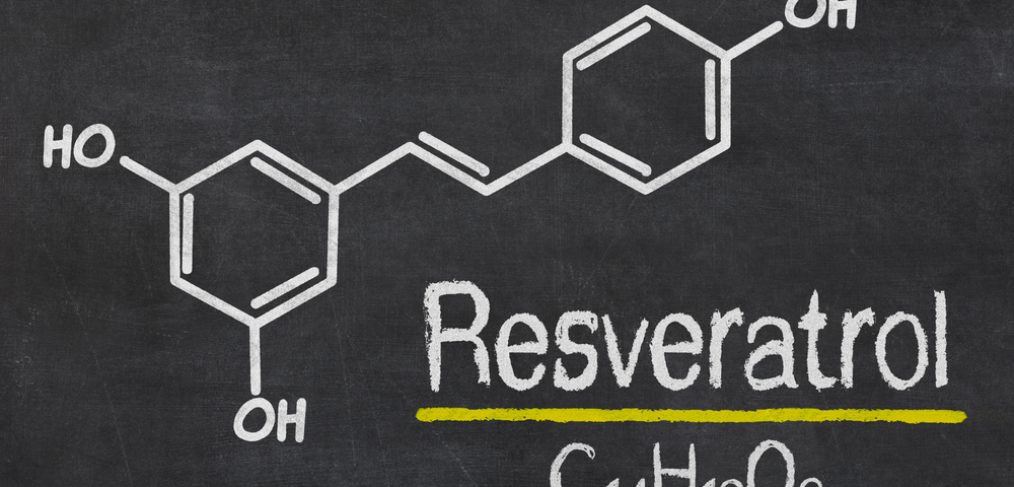
Resveratrol, an extremely popular polyphenol and highly effective antioxidant, has become immensely popular in the world of skin care. This ingredient already boasts of all sorts of studies that confirm the various benefits it has to offer and new benefits offered by the compound are being discovered with every passing year. Resveratrol is the ingredient that has been associated with the “French Paradox Theory” and it is usually derived from the skin of red grapes or from a plant known as Japanese Knotsweed. Resveralife decided to formulate its entire line of luxury skin care products around this miracle ingredient to help customers enjoy the very best of anti-aging and skin care.
Interest for Resveratrol exploded around the year 2003, when it was discovered that Resveratrol actually managed to increase the lifespan of yeast cells. This research once again ignited all those hopes and dreams of youthful looks and eternal beauty and experts began to compare it with the elusive Fountain of Youth. Over the years, other studies confirmed that Resveratrol also offered other benefits to the human body. The ingredient was reported to have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-diabetes properties and it is also known to offer cardiovascular benefits and protection against the Alzheimer’s disease.
Vine Vera was delighted to discover that scientists have recently discovered a more stable method for delivering Resveratrol. A group of researchers from the University of Massachusetts found out that extracts and oil from grape seeds, both of which are by-products of the wine industry, can be used to create stable nanoemulsions that can easily deliver Resveratrol and also protect the ingredient in food applications. The researchers reported that these nanoemulsions remained stable when they were stored at different temperatures, and that they also protected the Resveratrol from degradation and UV-light isomerisation.
The study was published in the Food Chemistry Journal, Volume 167 and it was authored by D.J. McClements and G. Davidov-Pardo. The researchers used orange oil (indigestible) and grape seed oil (digestible) to produce the nanoemulsion-based delivery system for Resveratrol. They discovered that the optimal combination of grape seed oil and orange oil was 1:1, which allowed the formation of droplets that have an average diameter of 100nm. They further confirmed that a maximum of 120 micrograms/ milliliter of Resveratrol dosage could be added to these delivery mechanisms.
According to the authors of the study, the results have shown that the nanoemulsions formed using spontaneous emulsifications can easily be used to encapsulate Resveratrol as a nutraceutical ingredient by combining wine industry by-products like grape skin extracts and grape seed oils. The authors believe that these nanoemulsions can prove to be extremely effective in creating delivery systems for Resveratrol in beverage and functional food products.
Reports suggest that the results of this study further verified that encapsulating Resveratrol helped in increasing the ingredient’s chemical stability after being exposed to UV-light. The nanoemulsions managed 88% retention as compared to the 50% retention seen in DMSO (dimethylsulphoxide) techniques used today.